Perfect Integration of Complex Sensors and Real-Time Machine Vision Analysis
Since the automated guided vehicle (AGV) must be deployed in a pre-planned environment, the overall deployment cost is relatively high and it is also difficult to cope with unexpected situations. For example, once an obstacle is encountered during transportation, the operation can only be suspended. Therefore, autonomous mobile robots (AMR) with independent guidance, machine vision, and map construction capabilities can automatically determine the most effective path and avoid obstacles. AMR's ability to overcome the barriers and environmental adaptability is becoming necessary for more complex plant and storage placement.
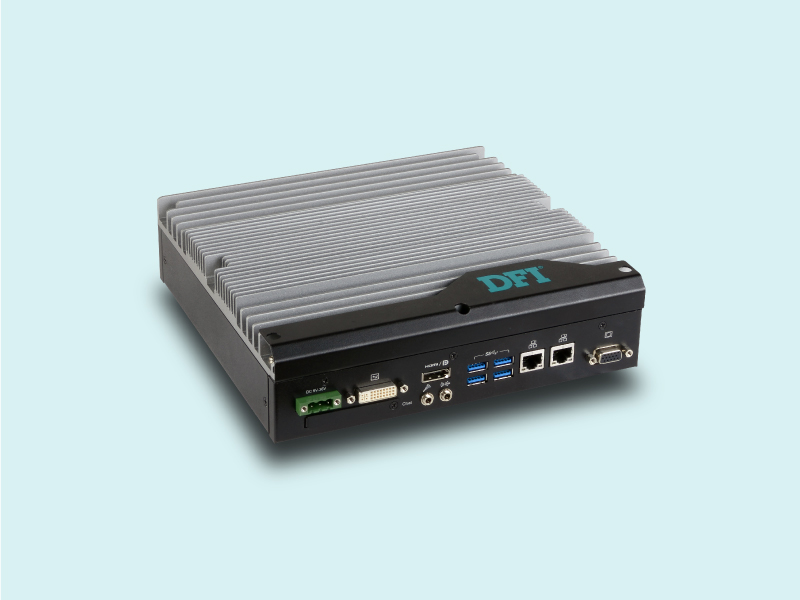
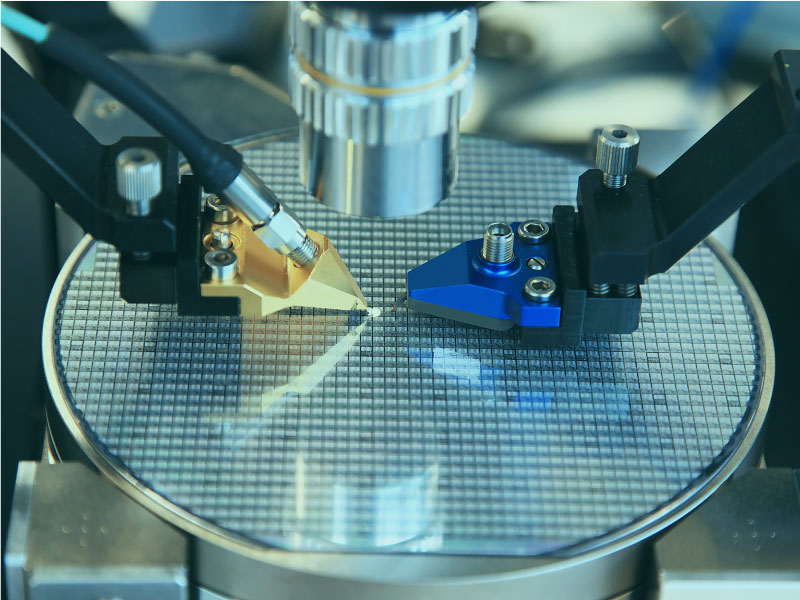
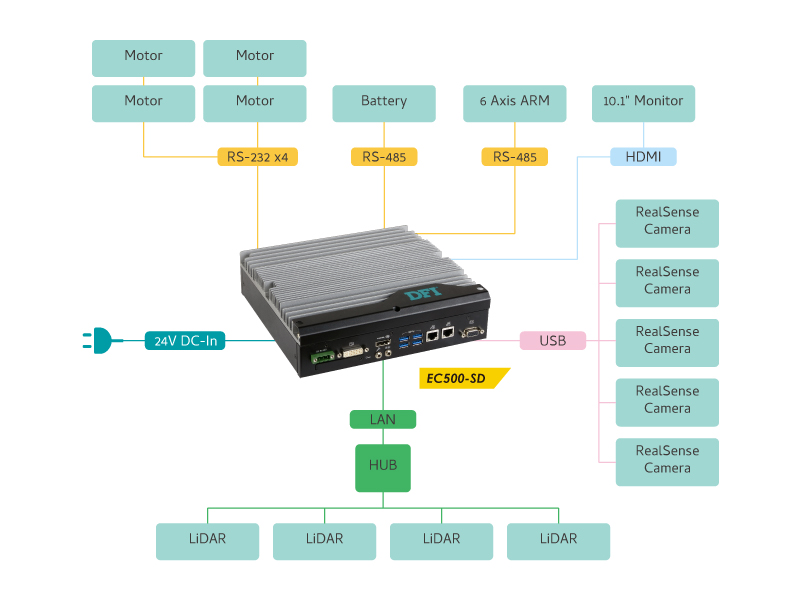
However, autonomous mobile robots need to integrate with more versatile sensors including depth cameras and laser radars for positioning, laser scanners to prevent long-distance collisions, ultrasonic sensors to detect short-distance collisions, and various wireless network specifications and control drives technology. A world-renowned IC packaging and testing company in Taiwan initially used an industrial computer solution. However, the number of COM ports and USB units was not enough to meet the demand, leading to the requirement for additional controllers.
In addition to the perfect integration of complex sensors, autonomous mobile robots must perform more complex real-time machine vision analysis, as well as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms, customized application programming interface (API), and higher system integration to ensure seamless compatibility and maximize execution performance. Finally, in order for IC packaging and testing to meet companies' production line operation requirements, industrial displays must be installed. This means that system integration (SI) services from industrial computer manufacturers are required to create the most well-designed autonomous mobile robot.




,有助於車隊管理員管理駕駛行為、運動感測、急煞車和衝擊偵測.jpg?timestamp=1689918406.42007)